Research Objectives:
To evaluate the impact of Transformational Leadership on school culture, and how it contributes to an inclusive and supportive school environment.
Keywords:
Transformational Leadership, School Culture, Teacher Innovation, Stakeholder, Student Outcomes
Bio
His Excellency Dr. Freddie A. Lee is a retired U.S. Army Officer, a former Educator, an award-winning Senior Defense Acquisition Test and Evaluation engineer, and a WOLMI United Nations Peace Ambassador. Dr. Lee has over 45 years of experience in developing, organizing, and implementing solutions to develop effective organizations. He is an expert in developing solutions across military, education, and corporate sectors. Dr. Lee has expertise in leadership development, team building, strategic planning, and technical evaluation. Dr. Lee served as an administrator at the historic St. Frances Academy in Baltimore, ensuring academic excellence and whole student support. His distinguished honors include recognition as the National Defense Industrial Association (NDIA) 2-time Contractor Tester of the year. Dr Lee has received several other recognitions, including the Gentlemen of Heart Award, Passion Purpose Peace Award, the Presidential Life-Time Achievement Award, for his impactful contributions, and the GOHA Esteemed First Gent Award in London England. Dr. Lee was also featured in Tap-In Magazine as part of the Men’s Hall of Fame.
Abstract
Transformational leadership has emerged as a pivotal approach in educational leadership, significantly influencing the forces that shape school culture and drive improvement. This research paper explores the intricate relationship between transformational leadership and school culture, focusing on how this leadership style impacts various aspects of the school environment. By examining its effects on administrators, staff collaboration, teacher innovation, and student outcomes, the paper highlights the multidimensional role of transformational leadership in fostering a positive and dynamic educational setting.
Through a comprehensive review of relevant literature and the analysis of case studies, the research underscores the ability of transformational leaders to inspire and empower stakeholders, creating an environment of trust, mutual respect, and shared vision. This approach enhances teacher performance by encouraging innovation, professional growth, and a sense of ownership. The ripple effect of transformational leadership extends to students, leading to improved academic achievements and overall well-being.
The study also delves into the collaborative culture fostered under transformational leadership, characterised by open communication, teamwork, and collective decision-making. By aligning the goals of stakeholders and addressing challenges proactively, transformational leaders play a crucial role in shaping an inclusive and sustainable school environment. This paper concludes that transformational leadership is not just a managerial style but a transformative force that can redefine educational success.
-
Introduction
Background on school culture and its importance
School culture refers to the shared beliefs, values, attitudes, and behaviours that characterise a school community. It encompasses the norms and expectations that shape how students, teachers, staff, and administrators interact and engage in the educational process. School culture is influenced by several factors. These include e community, demographics, educational policies, social, economic, cultural, and political influences, and most importantly, leadership styles. Student culture matters not only because it gives our students a solid foundation on which to learn but also because it’s our opportunity to communicate to our students how much we believe in them, and that we will support them in becoming their best self (Bambrick-Sanytoyo, 2018). School culture is essential to educating our students because it provides the foundation for learning. Effective leadership can produce a positive school culture, which is linked to improved student knowledge, skills, abilities, and attitudes, otherwise known as student outcomes.
Examples of these outcomes would include higher academic performance, increased motivation, and better attendance rates. A positive school culture is often associated with high levels of student achievement, strong teacher morale, and a supportive learning environment (Deal & Peterson, 1990). When students feel safe, valued, and engaged, they are more likely to succeed academically. In short, transformational Leadership is effective in having a positive impact on school culture. Figure 1 highlights the concepts of culture and climate according to the British Educational Research Journal.
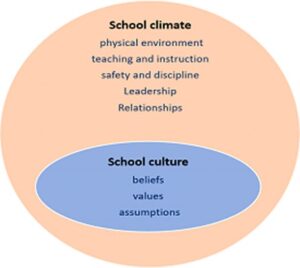
Figure 1 (Barker, et al., 2023)
Transformational leaders as conceptualized by(Burns (1978) and later expanded by Bass, (1985), are those who inspire followers to transcend their self-interests for the sake of the organisation. Bernard Bass developed four elements to transformational leadership: Intellectual Stimulation, Individual Consideration, Idealised Influence, and Inspirational Motivation (Bass 1985). Leaders who implement these elements in the workplace experience a more positive climate and culture. These leaders are charismatic, inspirational, intellectual, and show compassion and empathy. It is a leadership style that empowers people to execute changes through vision, inspiration, and by taking positive action. Leaders enable change by emotionally connecting with their audience and inspiring them to achieve something greater than themselves. Through communicating their vision for the organisation, transformational leaders influence, motivate and encourage their followers to continue to work towards the vision. The result is collaborative action that leads to innovation, massive transformation, that encourages, inspires, and motivates stakeholders (administrators, teachers, students, parents) to create necessary changes to shape the future success of an organisation. Transformation leaders inspire and motivate without micromanaging. They trust their stakeholders to take ownership of their roles and responsibilities. It is designed to give an educational staff the room to be creative, look into the future and find new solutions to old problems.
Aim:
The intent of this research paper is to evaluate the impact of Transformational Leadership on school culture, and how it contributes to an inclusive and supportive school environment.
-
Method
This study employs a systematic review of literature, scholarly articles, and case studies to investigate the effects of transformational school leadership on school culture and student outcomes. The systematic review approach is widely recognized in academic research for its ability to synthesise existing knowledge, identify trends, and address gaps in the literature. By analysing diverse sources, this method ensures a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
The systematic review began with a structured search strategy to identify relevant publications. Databases such as JSTOR, ERIC, and Google Scholar were utilized, focusing on peer-reviewed articles, theses, and case studies published within the last two decades. Keywords including “transformational leadership,” “school culture,” “teacher innovation,” “stakeholder collaboration,” and “student outcomes” were used to refine the search. Inclusion criteria encompassed studies directly addressing transformational leadership in educational contexts, with an emphasis on measurable impacts on school culture and student performance. Exclusion criteria were applied to avoid redundant or non-relevant publications.
The selected materials were critically evaluated using a thematic analysis approach, categorizing findings based on their relevance to leadership practices, school environment, teacher performance, and student outcomes. Case studies provided practical insights into the application of transformational leadership in diverse school settings, highlighting its role in fostering collaboration, innovation, and positive cultural shifts.
Additionally, this method integrates a comparative analysis of successful and unsuccessful implementations of transformational leadership, offering a balanced perspective. The findings from this review were triangulated to ensure reliability and validity, drawing connections between leadership practices and their implications for stakeholders within the school system.
By relying on this systematic approach, the study establishes a strong theoretical and empirical foundation, presenting a nuanced understanding of how transformational leadership impacts school culture and student outcomes, while offering practical recommendations for educational leaders.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Transformational Leadership in a Suburban School
In this case study, “Burton Middle School Improves Reputation and Enrollment Through Transformational Leadership Practices” (Studer Education.com, Huron Consulting Group 2024), the principal implementing transformational leadership practices successfully enhanced the school’s reputation, and increased student enrollment. Faced with declining enrollment and negative perceptions within the community, the school’s leadership team adopted a strategic approach focused on collaboration, innovation, and community engagement. Key initiatives included fostering a positive school culture, enhancing communication with parents and stakeholders, and involving teachers and staff in decision-making processes. Professional development programs were introduced to empower teachers, encouraging them to take ownership of their roles and contribute to the school’s vision. This approach bolstered the school’s reputation and created a more inclusive and supportive environment for students and staff alike. This case study highlights the importance of transformational leadership in driving meaningful change within educational institutions, showcasing how effective leadership can revitalize a school and positively impact its community.
Case Study 2: Transformational Leadership in a Challenging Environment
In an urban school grappling with significant challenges such as low student performance, high teacher turnover, and limited community engagement, the principal adopted transformational leadership strategies to initiate a cultural and operational shift. The principal began by focusing on individualised consideration, a core element of transformational leadership, ensuring that both teachers and students received personalised support tailored to their unique needs. Teachers were encouraged to voice their concerns and aspirations, fostering an inclusive environment where professional development opportunities were aligned with their goals. Students were provided with mentorship programs, counseling services, and academic support to address individual barriers to success.
Through clear communication of a shared vision, the principal inspired staff to embrace collaboration and innovation. According to research Kashyap, 2024 figure 2 highlights the seven C’s of effective communication include concrete, coherent, clarity, commitment, consistency, completeness and courteous.
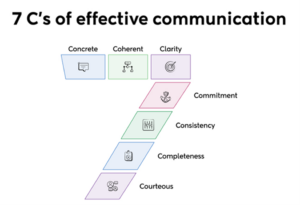
Figure 2 (Kashyap, 2024)
Weekly team meetings were introduced to encourage collective problem-solving, and professional learning communities were established to promote peer-to-peer learning and idea sharing. Simultaneously, parents were actively involved in school activities through workshops, volunteer opportunities, and consistent communication, enhancing their sense of belonging and investment in the school’s progress.
As a result, the school witnessed a positive cultural transformation. Relationships among staff became stronger, morale improved, and parents became more engaged in their children’s education. Most importantly, student achievement showed significant improvement, with higher test scores, reduced absenteeism, and increased graduation rates, illustrating the transformative potential of effective leadership in challenging environments.
-
Discussion/Results
Positive leadership fosters trust and collaboration by allowing positive leaders to create an atmosphere of trust which encourages open and transparent communication and collaboration among administrators and teachers. Trust facilities, teamwork and strengthened relationships are essential for a supportive school culture. Leaders who practice positive support help boost teacher morale. When educators feel valued and appreciated, they are more likely to be engaged, motivated, and committed to their roles, contributing to a positive school environment. In The Effects of Transformational Leadership on Organizational Conditions and Student Engagement with School (Leithwood and Jantzi 2000) found that schools with transformational leaders demonstrated higher levels of teacher collaboration and commitment, leading to improved student outcomes. There is a direct correlation between teacher morale and student engagement.
3.1 Influences of positive leadership on school Culture
Positive leadership emphasises the importance of inclusivity, ensuring that all perspectives and ideas are considered. This commitment to diversity fosters a culture where every student and teacher feels valued and included. Leaders who promote a positive culture encourage teachers to experiment with new teaching ideas and methods. This openness to innovation creates an environment that values growth and continuous improvement. Positive leaders articulate clear objectives and vision and set high expectations for both staff and students. They set high standards for academic and social performance, insist that all standards are achieved or exceeded, and help those struggling to meet the standard. This clarity helps to align efforts and creates a shared sense of purpose, enhancing overall school cohesion. Leaders who exhibit positive behaviors and attitudes set a standard for others to follow. Their actions can inspire staff and students to adopt similar behaviors, contributing to a more positive school culture. Positive leaders prioritise the emotional and physical safety of students and staff. By addressing issues such as bullying and harassment, they help create a supportive environment conducive to learning. Positive leadership involves actively listening to students and allowing them to participate in decision-making processes. This empowerment fosters a sense of belonging and ownership among students. Research by (McLeod, 2013) emphasises that schools led by transformational leaders often see increased student motivation and engagement, which are crucial for academic success. Acknowledging the achievements of staff and students fosters positivity and motivation. Celebrations of success help build a sense of community and reinforce a culture of appreciation. (Leithwood & Jantzi examined the practices of 12 school administrators who developed highly collaborative professional relationships over a three-year period, in the context of school improvement initiatives. The results revealed that developing more collaborative school cultures in a relatively brief period time fostered positive student outcomes and professional growth among teachers. Studies conducted by international scholars reveal that positive leadership plays a crucial role in shaping school culture by fostering trust, promoting inclusivity, encouraging collaboration and reacting to an environment where both educators and students can thrive.
3.2 Leadership practices that contribute to inclusivity and support?
Encouraging open and transparent communication among administrators, teachers, students, and parents fosters trust and allows for sharing of diverse perspectives. Leaders who create forums for dialogue, such as regular meetings and feedback sessions enable stakeholder input and involvement. Encouraging teachers, students, and parents to participate in the decision-making processes promotes a sense of ownership and belonging. Leaders who establish committees or task forces that include various stakeholders will ensure that diverse voices are heard. Understanding and valuing the diverse cultural backgrounds of students and staff is crucial. Leaders must engage in professional development on cultural competence and ensure that school policies reflect this understanding. In “Visible Learning,” (Hattie emphasises the importance of visible learning, where both teachers and students are aware of their learning goals and progress. Hattie ranks various influences on achievement, highlighting that factors such as teacher-student relationships, feedback, and clear learning intentions are among the most impactful.
Providing ongoing training focused on inclusivity, equity, and social justice equips staff with the tools, skills, and knowledge required to recreate an inclusive environment.
School leaders should consider implementing mentorship programs for staff and students to foster a supportive environment. Pairing experienced educators with newer teachers or offering peer support for students enhances personal and professional growth. Leaders must recognise and accommodate the diverse needs of students, including those with disabilities, English language learners, and students from various socioeconomic backgrounds. This may involve adjusting the curriculum, providing additional resources, or offering specialised support.
Schools that celebrate diverse cultures, traditions, and achievements of students and staff help create an inclusive atmosphere. Leaders can organise cultural events, recognition programs, and inclusive curricula that reflect the community’s diversity. Cultivating positive relationships with students, staff, and families is essential. Leaders should prioritise regular interactions and check-ins to understand the needs and concerns of all stakeholders.
By establishing safe and supportive environments where students and staff can express their identities without fear of discrimination, school leaders will stimulate a positive atmosphere throughout the school environment. Along the same line, establishing and enforcing anti-bullying policies and nurturing respect for all will help to strengthen a positive school culture.
Encouraging regular feedback from students and staff about the school environment and leadership practices helps identify areas for improvement. Leaders should be open to constructive criticism and willing to adapt based on feedback. Ensuring that there is equitable access to resources, including technology, material and support services, is essential for creating an inclusive environment. Leaders should advocate for resources that meet the diverse needs of their school community. Articulating a clear vision and set of values that emphasise inclusivity, and support establishes the foundation for school culture. Leaders should consistently communicate and model these values in their practice. By implementing these practices, school leaders can foster a culture of inclusivity and support, positively impacting the overall school environment for both students and staff.
3.3 Significance of the Research
Researching the role of transformational leadership in fostering a supportive and inclusive school environment is significant for several reasons. Understanding the dynamics of transformational leadership can help identify effective practices that lead to improved student outcomes, enhanced engagement, and overall well-being within school settings. Investigating this relationship provides valuable insights into how positive leadership influences teacher morale, job satisfaction, and retention rates, all of which are critical for maintaining a stable and effective teaching workforce.
This research highlights strategies employed by transformational leaders to promote diversity, equity, and inclusion, ensuring that all students feel valued and supported, particularly in increasingly diverse educational environments. By identifying the characteristics of transformational leadership that contribute to a positive school culture, this study can help schools create environments conducive to learning, collaboration, and innovation.
The findings of this research have practical implications for professional development programs, equipping school leaders with the skills and knowledge to implement transformational leadership practices effectively. Additionally, the study can influence educational policy by providing evidence-based recommendations for leadership practices that foster supportive and inclusive environments, aiding policymakers in making informed decisions.
Furthermore, understanding how transformational leaders shape school culture can build trust among stakeholders, including students, parents, and community members, fostering stronger partnerships. This research also sheds light on how transformational leadership can address systemic inequities in education, ensuring equitable access to quality education and resources for all students.
Ultimately, insights from this research contribute to the development of sustainable leadership practices that promote continuous improvement and adaptability in an evolving educational landscape. It also refines theoretical models of educational leadership, emphasising the importance of transformational leadership in achieving inclusive and supportive school environments. In conclusion, exploring the impact of transformational leadership is vital for enhancing educational effectiveness, promoting equity, and fostering environments where both students and educators can thrive.
-
Conclusion
This research concludes that transformational leadership has a positive impact on school culture, by creating a supportive school environment that is inclusive, fostering collaboration, innovation, which focuses on a shared vision of student accomplishment. Effective leaders create a compelling vision that inspires and motivates others (McLeod, S. 2013). Transformational leadership fosters a positive school climate by promoting trust, collaboration and open communication among staff and students. Leaders who inspire and motivate can create an environment where everyone feels valued. They encourage administrators and teachers to embrace professional development and take ownership of their roles and responsibilities, resulting in higher levels of performance, increased job satisfaction, and better retention. Transformational leaders focus on developing the capacity of their staff through mentoring, coaching and professional development, strengthening the overall effectiveness of the school.
Transformational leaders actively advocate for diversity, equity, and inclusivity within the school. They implement strategies that address the needs of all students, fostering an environment where every individual feels respected and included. These leaders articulate a clear and compelling vision for the school, aligning the efforts of staff and students towards common goals. This shared vision enhances collective responsibility and strengthens the school community.
Transformational leadership encourages the formation of professional learning communities, where educators collaborate, share best practices, and support each other’s growth. This collaboration promotes a culture of continuous improvement. These leaders exhibit high emotional intelligence. Which allows them to connect with staff and students on a personal level. This connection contributes to a sense of belonging and psychological safety with the school. This research indicates that schools led by transformational leaders often see improved student achievement and engagement. The supportive culture created by these leaders enables students to thrive academically and socially. They create an environment that encourages innovation and creativity in teaching practices. This flexibility allows educators to adapt to the diverse needs of students, enhancing inclusivity. The positive changes initiated by transformational leaders tend to be sustainable over time, as they built a strong foundation of shared values and practices that continue to influence school culture.
-
Recommendations
To harness the potential of transformational leadership in fostering a supportive and inclusive school environment, several key recommendations are proposed. These strategies aim to enhance collaboration, inclusivity, and professional growth, benefiting both educators and students:
- Develop a Shared Vision:
School leaders should work collaboratively with staff, students, and the community to establish a clear and compelling vision emphasizing inclusiveness and support. Aligning stakeholder efforts under this vision ensures unified progress. As Ryan (2010) notes in Promoting Inclusiveness in Schools: A Global Perspective, “True inclusiveness thrives on collaboration between teachers, families, and communities, creating a support network that empowers every student.” - Foster Open Communication:
Establish transparent channels for regular feedback and dialogue among stakeholders. Open communication allows leaders to understand and address the needs and concerns of staff and students, fostering trust and a supportive environment. - Invest in Transformational Leadership Training:
Offer comprehensive training programs focusing on the core components of transformational leadership—Intellectual Stimulation, Individual Consideration, Idealized Influence, and Inspirational Motivation. These programs should also emphasize emotional intelligence, communication, and conflict resolution, equipping leaders to inspire and motivate effectively. Ryan (2010) highlights, “Teachers must be equipped with the knowledge and skills to adapt their methods, ensuring they meet the diverse needs of their students.” - Enhance Soft Skills:
Provide annual training in emotional intelligence, communication, collaboration, organization, and creativity for school leaders. As Lee (2024) explains, “Organization is the ability to plan, prioritize, and manage tasks effectively. Organized leaders contribute to a positive climate and culture.” - Establish Professional Learning Communities:
Encourage the formation of professional learning communities where educators collaborate, share best practices, and support one another. This approach enhances inclusivity and promotes professional growth. - Empower Teachers and Staff:
Create opportunities for teachers to take on leadership roles and responsibilities. Empowering staff to participate in decision-making processes fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to the school’s mission. - Promote Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI):
Actively implement policies and practices that advance DEI, including cultural competence training and bias reduction for both staff and students. Such initiatives ensure an equitable and inclusive learning environment for all.
By adopting these recommendations, schools can effectively utilise transformational leadership to cultivate an inclusive culture, foster professional development, and improve outcomes for educators and students alike.
REFERENCES
Bambrick-Santoyo, P. (2018). Leverage leadership 2.0: A practical guide to building exceptional schools. Jossey-Bass.
Barker, R., Hartwell, G., Egan, M., & Lock, K. (2023). The importance of school culture in supporting student mental health in secondary schools. Insights from a qualitative study. British Educational Research Journal, 49, 499–521.
Bass, B. M. (1985). Leadership and performance beyond expectations. Free Press.
Björk, L. G., & Ginsberg, R. (1994). The role of the principal in creating a positive school climate. Educational Leadership, 52(1), 26–29.
Björk, L. G., & Richardson, M. D. (1997). Institutional barriers to educational leadership training: A case study. The Educational Forum, 62.
Burns, J. M. (1978). Leadership. Harper & Row.
Day, C., & Sammons, P. (2016). Successful school leadership: Linking learning and achievement. London: Open University Press.
Deal, T. E., & Peterson, K. D. (1990). The leadership paradox: Balancing logic and emotion in school leadership. Jossey-Bass.
DuFour, R., & Eaker, R. (1998). Professional learning communities at work: Best practices for enhancing student achievement. Bloomington, IN: Solution Tree Press.
Fullan, M. (2001). The new meaning of educational change. New York: Teachers College Press.
Hattie, J. (2009). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. New York: Routledge.
Kashyap, S. (2024). What is effective communication? [with benefits and tips]. Worklife.
Lee, F. (2024). The essential soft skills for effective leadership – Steps to leading with grace. Maryland: TAM Creating Ambassadors of Peace.
Leithwood, K. A., & Jantzi, D. (2000). The effects of transformational leadership on organizational conditions and student engagement with school. Journal of Educational Administration, 38(2), 112–129.
McLeod, S. (2013). Leadership for learning: A transformational approach. Educational Leadership and Administration: Teaching and Program Development, 25(2), 105–114.
Ryan, J. (2010). Promoting inclusiveness in schools: A global perspective. New York: Routledge.
Sergiovanni, T. J. (2000). The lifeworld of leadership: Creating culture, community, and personal meaning in our schools. Jossey-Bass.
Sergiovanni, T. J. (2001). Leadership: What’s in it for schools? London: Routledge Falmer.
Studer Education.com, Huron Consulting Group. (2024). Case study: Burton Middle School improves reputation and enrollment through transformational leadership practices.



