Research Objectives
Examine the causes, implications, and potential solutions to address pressing issues pertaining to illegal immigration in India.
Keywords
Illegal immigration, India, Border security, Conflict mitigation, International cooperation.
Bio
Dr Leena Dhankhar serves as the Chief Correspondent at Hindustan Times in Gurugram, where she has been a dedicated member since 2011. Specialising in crime coverage, Leena has amassed invaluable knowledge in this area, contributing extensively to the newspaper’s investigative Journalism. Currently, she oversees special investigations, excise matters, court proceedings, civic issues, district administration, Jails, and child rights concerns. With a meticulous attention to detail, Leena’s investigative stories on topics such as gangsters, child rights, Juvenile issues, and weapons have been particularly impactful. Over the past 13 years, she has played a pivotal role in addressing social issues and raising awareness about ground realities in the city through her insightful articles. Leena’s enthusiasm and determination shine through in her work, setting her apart as a standout Journalist in her field.
Abstract
Illegal immigration poses significant challenges for India, impacting its economy, society, and security. This paper aims to examine the causes, implications, and potential solutions to address this pressing issue. Various factors, including economic disparities, political instability, and porous borders, contribute to the influx of illegal immigrants into India. To investigate these issues, a mixed-method approach combining qualitative and quantitative analysis was employed. Data was gathered through literature and experts in the field. The results revealed that illegal immigration has far reaching implications, ranging from strain on resources and infrastructure to heightened social tensions and security threats. To tackle this issue effectively, a multi-pronged approach is necessary. This includes strengthening border security measures, improving diplomatic relations with neighbouring countries, enhancing intelligence sharing and cooperation, implementing stricter immigration policies and enforcement mechanisms, promoting socio-economic development in source countries, and facilitating legal pathways for migration. Additionally, addressing root causes such as poverty, unemployment, and conflict is essential to mitigate the drivers of illegal immigration. Through the adoption of comprehensive strategies and fostering international cooperation, India can better manage and mitigate the challenges posed by illegal immigration, thereby safeguarding its interests and promoting sustainable development.
Introduction
Illegal immigration poses significant challenges for India, impacting its socio-economic fabric, security, and diplomatic relations.
With porous borders and diverse socio-economic conditions, India faces complex dynamics that contribute to the phenomenon of illegal immigration.
Understanding the causes, implications, and potential solutions is imperative for effective policy formulation and implementation. This paper explores the multifaceted nature of illegal immigration in India, shedding light on the socio- economic drivers, security concerns, and diplomatic ramifications. By analysing the root causes and exploring the implications across various sectors, including economy, security, and social cohesion, this study aims to provide insights into the gravity of the issue.
Moreover, this paper examines potential solutions, ranging from enhanced border security measures to socio-economic development initiatives. It also emphasises the importance of international cooperation and diplomatic engagements in addressing illegal immigration comprehensively.
By delving into these aspects, this study seeks to contribute to the discourse on tackling illegal immigration in India, offering actionable recommendations for policymakers, law enforcement agencies, and other stakeholders.
This research paper focuses on six questions that could facilitate tackling illegal immigration in India:
- What are the primary push and pull factors driving illegal immigration into India, and how do they vary across different regions and demographics?
- What are the socio- economic implications of illegal immigration on Indian communities, labour markets, and public services, and how do these impacts differ between urban and rural areas?
- How does illegal immigration affect national security concerns, including border management, terrorism, and transnational crime, and what measures can be implemented to mitigate these risks?
- What diplomatic challenges does India face in addressing illegal immigration, particularly in relation to neighbouring countries and international migration flows?
- What policy interventions and institutional reforms are needed to enhance border security, streamline immigration processes, and address the root causes of illegal immigration effectively?
- How can India foster international cooperation and partnerships to tackle illegal immigration, including sharing best practices, intelligence sharing, and collaborative initiatives with other countries and international organisations?
2.0 Overview of the illegal immigration in India for the USA and Canada
Illegal immigration in India presents multifaceted challenges, impacting not only India but also neighbouring countries and regions. While the majority of illegal immigrants from India primarily seek opportunities in countries like the USA and Canada, there are various push and pull factors driving this phenomenon.
Push factors include economic disparities, lack of employment opportunities, poverty, and social unrest in India. Pull factors in destination countries like the USA and Canada include the promise of better economic prospects, higher wages, social welfare benefits, and opportunities for family reunification.
Illegal immigration poses significant socio-economic, security, and political challenges for both India and destination countries. In India, it strains public resources, affects job markets, and contributes to social tensions. Additionally, porous borders and inadequate immigration controls raise concerns about national security and facilitate transnational crime and terrorism.
For destination countries like the USA and Canada, illegal immigration creates pressures on social services, strains infrastructure, and raises questions about national identity and cultural assimilation. Moreover, undocumented migrants often work in sectors such as agriculture, construction, and hospitality, leading to debates about labour rights, wages, and job competition among native workers.
Addressing illegal immigration requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing border security measures, immigration reforms, diplomatic cooperation, and efforts to address root causes such as poverty, inequality, and political instability. Collaborative initiatives between India, the USA, and Canada are essential to manage migration flows, enhance information sharing, and promote legal pathways for migration while combating human trafficking and smuggling networks.
Historically, factors such as economic disparities, political instability, social unrest, and regional conflicts have been primary drivers of illegal immigration from India. These factors have prompted individuals and families to seek better opportunities and living conditions abroad, often resorting to irregular means due to limited legal pathways for migration.
During the mid-20th century, events such as the partition of India in 1947 and subsequent communal tensions led to population movements within the Indian subcontinent. Additionally, economic hardships in post-independence India prompted some individuals to seek opportunities in other countries, including those in Europe, North America, and the Middle East.
In more recent decades, globalisation, advancements in transportation and communication technology, and increasing interconnectedness have facilitated greater mobility and migration from India to various parts of the world. However, alongside legal channels of migration, there has also been a continued flow of illegal migrants seeking better economic prospects, employment opportunities, and social welfare benefits in destination countries. While illegal immigration from India is not a recent phenomenon, its scale and dynamics have evolved over time in response to changing socio-economic and geopolitical conditions both within India and in destination countries.
2.0 Data of migrants that illegally crossed borders
The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) last year in December 2023 disclosed in Parliament that US authorities encountered more than 200,000 illegal Indian immigrants over the past five years (Economictimes, 2023). The data presented by Minister of State for External Affairs V Muraleedharan revealed a significant increase, with the highest number of cases, 96,917, reported in 2022-23 (Dieterich, 2023). The figures indicate a notable rise from previous years, with 8,027 encounters in 2018-19, 1,227 in 2019-20, and a substantial surge to 30,662 in 2020-21. The number in 2021-22 was 63,927 while 96,917 cases were reported in 2022-23 (Patel, 2024). The total number of illegal Indian immigrants encountered by the American authorities comes to 200,760 (Economictimes, 2023). Figure 1 illustrates the number of migrant deaths in the Americas in 2022, marking it as the deadliest year on record since the inception of IOM’s Missing Migrants Project (MMP) in 2014. On 21st December 2023 a Legend Airlines flight departed from Dubai with 303 Indian passengers headed for Nicaragua in Central America. However, the journey took an unexpected turn when the flight made a technical stop at Vatry airport in France, about 160 km from Paris.
French authorities, acting on information suggesting possible human trafficking, intervened upon the flight’s arrival (Ernst, 2024). The airport was quickly transformed into a makeshift tribunal, with judges and lawyers summoned for emergency hearings. All 303 passengers, Indian citizens who boarded the flight in the UAE, were called before a judge. Liliana Bakayoko, the airline’s lawyer, confirmed the seriousness with which French authorities treated the situation but did not disclose the source of the tip-off regarding possible trafficking activity.
3.0 The Plight of Illegal Immigration
In the heart of Gujarat’s Mehsana district the Chaudhary family, comprising Praveenbhai, Dakshaben,
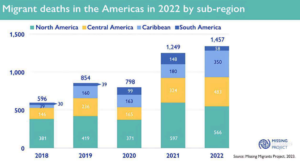
Figure 1. (IOM, 2023)
Meet, and Vidhi, embarked on a journey that was supposed to lead them to greener pastures. However, their quest for a better life took a tragic turn when they attempted to cross the border into the United States from Canada, only to meet their untimely demise in the icy waters of the St. Lawrence River.
Their story is just one among many in a string of incidents highlighting the perils of illegal immigration. For the Chaudharys, like countless others, the promise of a brighter future lured them into the clutches of human traffickers who promised to facilitate their passage to the US. With tourist visas in hand and hope in their hearts, they set out on a perilous journey that would ultimately end in tragedy.
But theirs is not an isolated case. The Dingucha incident, which shocked the nation in January 2022, saw another family freeze to death while attempting a similar journey. The harsh realities of illegal immigration came to the forefront once again, as Jagdish Patel, Vaishali, Vihanga, and Dharmik succumbed to the unforgiving cold in a desolate field in Canada.The pursuit of better opportunities abroad has driven many to take desperate measures, risking life and limb in search of a brighter tomorrow. Brijkumar Yadav’s fatal fall from the US-Mexico border wall, while carrying his young son, serves as a grim reminder of the dangers that await those who dare to tread the path of illegal immigration.
Yet, behind these tragedies lies a network of exploitation and deceit where individuals face death (India, 2022). Masterminds of illegal immigration rackets, prey on the hopes and aspirations of vulnerable individuals, charging exorbitant fees for passage to foreign lands. Despite crackdowns by law enforcement agencies, the allure of a better life overseas continues to drive many to pursue illegal immigration routes, often with devastating consequences. As Gujarat grapples with the aftermath of yet another tragedy, questions abound about the efficacy of measures to curb illegal immigration and the role of human traffickers in perpetuating this cycle of despair.
Illegal immigration routes to the United States and Canada vary depending on geographic proximity and the tactics employed by human traffickers. Some of the common routes include:
Southern Border (US- Mexico):
This is one of the most well known routes for illegal immigration into the United States. Migrants from Central and South America, as well as other regions, often attempt to cross the US-Mexico border on foot or by other means, sometimes with the assistance of human smugglers.
St. Lawrence River (US- Canada):
In recent years, there have been incidents of migrants attempting to cross the St. Lawrence River from Canada into the United States. This route poses significant dangers, especially during colder months when the water is icy.
Central and South America:
Some migrants from countries outside the Americas may travel to Central or South American countries before attempting to enter the United States or Canada. This may involve multiple stages of travel, including flights, land crossings, and possibly sea routes.
Caribbean Islands:
Some migrants may travel to Caribbean islands before attempting to reach the United States or Canada. This could involve travel by boat or other means to nearby countries with closer proximity to the target destination.
Europe and South America:
The “donkey route,” as it is sometimes called, involves a multi-hop journey through Europe and South American countries before reaching the United States or Canada (Dhankhar, Paid 1st tranche in 2020 to embark on donkey route, 2024).
This route may include stops in countries such as France, Nicaragua, and Mexico, often with the assistance of human traffickers who provide fake documents and other support (Dhankhar, Donkey route flyers knew of risks, pitfalls, 2022).
These are just a few examples of the routes used by migrants attempting to enter the United States and Canada illegally. The choice of route may depend on factors such as geographic proximity, ease of access, and the tactics employed by human traffickers.
3.1 Families of Missing Individuals Still Grappling in Pain
The families of victims who are still missing continue to grapple with profound pain and uncertainty. Their anguish is palpable as they endure the agonising wait for news, clinging to hope while fearing the worst. Each passing day brings a relentless cycle of despair, as they struggle to come to terms with the absence of their loved ones.
The emotional toll of not knowing the fate of their family members weighs heavily on these grieving families. Every unanswered phone call, every knock on the door, fills them with a sense of dread, amplifying their sense of helplessness and despair. They yearn for closure, for any shred of information that might offer them solace and a semblance of peace.
Amidst their pain, these families cling to hope, drawing strength from each other and from the unwavering support of their communities. They rally together, united in their quest for answers and justice, refusing to let their loved ones fade into oblivion. Their resilience in the face of adversity serves as a beacon of light in the darkness, a testament to the power of love and solidarity in the face of unimaginable loss.
In the quiet village of Vaghpur, Bharat Desai, a hardworking farmer with dreams as vast as the endless skies above his land, embarked on a journey one fateful January morning in 2022. Like so many others before him, Bharat’s aspirations carried him far beyond the borders of his homeland, fueled by the promise of opportunity and prosperity that seemed to beckon from distant shores. But the path to a better life was fraught with deception and betrayal, as Bharat fell victim to the machinations of unscrupulous agents who promised him the world and delivered only heartache. Sold to the highest bidder, his dreams were dashed against the jagged rocks of exploitation, leaving behind a trail of broken promises and shattered lives. For Bharat’s wife, the pain of separation cuts deep, as she grapples with the silence that has enveloped her once vibrant home. Each day brings with it a renewed sense of anguish, as she waits for news of her husband, lost in a sea of uncertainty and despair. The story is not unique to the Desai family alone, as eight other families from Gujarat share in their anguish and despair.
Yet, amidst the darkness, there is a glimmer of hope, as these families unite in their quest for justice and closure. Their voices, though muffled by grief, rise in defiance against the forces that seek to silence them, as they demand answers and accountability from those who preyed upon their hopes and dreams (Portal, 2024). Their journey is far from over, but their resolve remains unbroken, as they continue to fight for the truth and for the closure they so desperately seek.
In India, particularly from states like Gujarat, Punjab, Haryana, and others, individuals often pay exorbitant sums to take illegal routes to reach the United States or Canada. These illegal immigration routes involve complex networks of agents and smugglers who exploit aspirations of desperate individuals seeking better opportunities abroad. Here’s an overview of how the process works:
Document Forging:
Agents assist individuals in obtaining forged documents like passports, visas, educational certificates, job papers, and sponsor letters (Dhankhar, Forged papers, long route: Rush of FIRs reveal tip of immigration racket iceberg, 2024). These documents are often fabricated to make it appear as though the individual meets the legal requirements for entry into the destination country.
Visa Acquisition:
For individuals lacking the necessary qualifications or documentation, agents arrange for visas through illicit means. This may involve obtaining visas for transit countries that have agreements allowing visa- on-arrival for certain passport holders. For example, Mexico and Nicaragua allow Indians to obtain visas on arrival if they have valid visas for other countries like the UK or Schengen area countries.
Illegal Transportation: Once the necessary documents are acquired, individuals are transported through various countries using irregular methods. This may include air travel with multiple stopovers in different countries to avoid detection, or even land or sea routes that circumvent official border checkpoints. Figure 2 highlights the access of illegal migrants to road freight transport units.
Figure 2. (Lietuvnikė, Vasilis Vasiliauskas, Vasilienė-Vasiliauskienė, & Sabaitytė, 2018)
Transit and Rented Accommodations:
During transit, individuals are often housed in rented apartments in cities like Dubai or Istanbul. These locations serve as temporary holding areas where migrants await further instructions or transportation to their final destination.
Crossing Borders:
The final leg of the journey typically involves crossing the US-Mexico border or entering Canada through illicit means. This may entail dangerous border crossings through remote areas or maritime routes that evade official surveillance (Malkin, 2022).
Exploitation and Debt: Individuals who undertake these illegal journeys often accrue significant debts to the agents and smugglers facilitating their travel. These debts can amount to lakhs of rupees, placing immense financial strain on the migrants and their families. Moreover, migrants may become vulnerable to exploitation and abuse during their journey, with little recourse to legal protection.
Overall, the illegal immigration process from India to the US or Canada is characterized by deception, exploitation, and high levels of risk. Despite the potential dangers and legal consequences, many individuals are willing to pay substantial sums and endure hardships in pursuit of the elusive promise of a better life abroad (Landa, 2023).
3.2 Why Do people risk their lives despite knowing the risks
People risk their lives and pursue illegal routes to cross borders and enter countries like the US and Canada due to a combination of push and pull factors. Here are some reasons why individuals take such risks:
Economic Opportunities:
Many individuals from countries like India see migrating to countries like the US and Canada as a means to access better economic opportunities. They believe that by moving to these countries, they can secure higher- paying jobs, improve their standard of living, and provide a better future for their families.
Social Pressures:
In some cases, societal pressures play a significant role in driving individuals to migrate illegally. Families may face pressure from their communities to send a member abroad in pursuit of better prospects, especially if they see others around them benefiting from such moves.
Lack of Legal Avenues:
Limited access to legal pathways for migration can lead individuals to resort to illegal means. Stringent immigration policies, long wait times for visas, and high costs associated with legal migration channels can push people towards undocumented routes as a quicker alternative.
Deception by Traffickers:
Individuals may fall victim to false promises made by human traffickers or agents who exploit their dreams of a better life abroad (Gupta, 2022). Traffickers lure vulnerable migrants with assurances of smooth passage, job opportunities, and a comfortable life in destination countries, only to exploit them for financial gain.
Desperation:
Some migrants may feel desperate due to dire circumstances in their home countries, such as poverty, political instability, or conflict. They may see illegal migration as their only option for escaping these challenging conditions and seeking a better future elsewhere.
Family Obligations:
Family members already residing in countries like the US or Canada may encourage or pressure their relatives back home to join them, promising support and assistance upon arrival. This familial obligation can motivate individuals to undertake risky journeys despite the dangers involved.
Despite knowing the risks and the potential consequences, individuals often choose to take the illegal route in the hope of achieving their aspirations for a better life for themselves and their families.
Combating Illegal Immigration: Society and Government Unite to Address Migration Challenges
Controlling illegal immigration requires a multi-faceted approach involving both societal and governmental efforts. Here are some ways in which society and the government can collaborate to address this issue:
Public Awareness Campaigns:
Educate the public about the risks and consequences of illegal immigration through targeted awareness campaigns. Provide information about legal migration pathways, including visa programs and immigration policies, to empower individuals to make informed decisions.
Crackdown on Trafficking Networks:
Strengthen law enforcement efforts to dismantle human trafficking networks and prosecute individuals involved in smuggling migrants. Increase cooperation between national and international law enforcement agencies to disrupt illegal migration routes and apprehend traffickers.
Support for Vulnerable Communities:
Provide support and assistance to vulnerable communities that are susceptible to exploitation by traffickers. Offer economic opportunities, social services, and educational programs to address the root causes of migration and reduce reliance on illegal pathways.
Enhanced Border Security:
Invest in technology, infrastructure, and personnel to enhance border security measures and prevent unauthorized entry into the country. Implement stricter border controls, surveillance systems, and patrols to deter illegal crossings and apprehend individuals attempting to enter illegally.
Addressing Push Factors:
Address the underlying push factors driving individuals to migrate illegally, such as poverty, unemployment, political instability, and lack of economic opportunities. Invest in economic development, job creation, and poverty alleviation initiatives in source countries to reduce the incentive for illegal migration.
Streamlined Immigration Processes:
Simplify and streamline legal immigration processes to make them more accessible and efficient for migrants Reduce bureaucratic barriers, processing times, and visa fees to encourage individuals to pursue legal migration pathways instead of resorting to illegal means.
International Cooperation:
Foster international cooperation and collaboration to combat illegal immigration on a global scale. Strengthen diplomatic relations, share intelligence and information, and coordinate efforts with other countries to address transnational migration challenges effectively.
Conclusion
By implementing a comprehensive approach that combines prevention, enforcement, and support measures, society and the government can work together to control illegal immigration and protect vulnerable migrants from exploitation and harm.
The countries experiencing higher levels of illegal immigration often include those with economic disparities, political
Crackdown on Trafficking Networks:
instability, or armed conflicts, as individuals seek better living conditions or safety. Some countries known for facing challenges related to illegal immigration include:
United States:
Border Issues: The U.S.- Mexico border is a focal point of discussions on illegal immigration. Migrants often attempt to cross the border without proper documentation, leading to concerns about border security.
Diverse Causes: Economic opportunities, family reunification, and fleeing violence or persecution are common reasons for individuals seeking to enter the U.S. illegally.
Policy Changes: Changes in U.S. immigration policies can impact the patterns of illegal immigration. Shifts in administrations often bring adjustments to border control measures and immigration regulations.
European Union Countries:
Mediterranean Routes: Countries like Greece, Italy, and Spain face challenges related to migrants attempting perilous journeys across the Mediterranean Sea.
Refugee Crisis: The EU experienced a significant influx of refugees and migrants, especially during the Syrian refugee crisis. Addressing humanitarian needs while managing immigration has been a complex task.
Mexico:
Transit Country: Mexico serves as a transit country for individuals from Central America en route to the United States. The country faces challenges in managing and regulating this migration flow.
Greece, Italy, Spain:
Geographic Challenges: Being geographically positioned at the crossroads of Africa, the Middle East, and Europe, these countries are often entry points for migrants attempting to reach European soil.
Asylum Seekers: Many individuals arriving irregularly seek asylum, posing challenges in processing claims and addressing humanitarian needs.
Australia:
Boat Arrivals: Australia has faced issues related to individuals arriving by boat, often making dangerous journeys. The country has implemented strict border control measures to deter such arrivals.
The challenges associated with illegal immigration include humanitarian concerns, strained resources, and debates over immigration policies. Countries affected often grapple with balancing border security and humanitarian obligations, seeking comprehensive and sustainable solutions. International cooperation is crucial in addressing the root causes of migration and managing the global impact of illegal immigration. The “way forward” refers to the recommended actions or strategies to address the challenges discussed in the paper. In the context of tackling illegal immigration in India, here are some potential “way forward” strategies:
Enhanced Border Surveillance:
Implement advanced technologies such as drones and sensors for more effective border monitoring. Increase personnel, patrols, and checkpoints at vulnerable border areas. Utilize satellite technology and real-time data analytics to improve situational awareness.
Strengthened Law Enforcement Measures:
Provide specialized training to law enforcement agencies to combat human trafficking and illegal immigration. Establish dedicated task forces to investigate and dismantle smuggling networks. Increase penalties for individuals involved in human trafficking and those hiring undocumented workers.
Promoting Economic Development:
Focus on economic development initiatives in regions with high emigration rates to create job opportunities. Encourage foreign investment and entrepreneurship to stimulate local economies. Implement skill development programs to enhance employability in vulnerable regions.
International Cooperation:
Engage in diplomatic efforts with countries of origin to address root causes of migration, such as economic instability and violence. Strengthen international cooperation on border control and information sharing. Collaborate with neighboring nations to develop regional strategies for managing migration flows.
Policy and Legal Reforms:
Review and update immigration laws to make them more effective and responsive to current challenges. Simplify legal immigration processes to encourage people to choose legal avenues. Ensure that existing laws are consistently enforced and consider amendments where necessary.
Media’s Role in Raising Awareness:
Collaborate with the media to raise public awareness about the risks and consequences of illegal immigration. Disseminate information about legal immigration channels and available support services. Encourage responsible reporting that highlights the complexities of the issue and promotes informed public discourse.
Community Engagement and Outreach:
Establish community outreach programs to build trust and cooperation between law enforcement agencies and local communities. Involve community leaders in spreading awareness and advocating for legal immigration channels. Provide support services for families affected by illegal immigration.
Investment in Technology:
Utilize digital systems for visa processing and immigration management to streamline procedures. Invest in research and development of technology solutions to enhance border security. Explore collaborations with technology companies for innovative solutions.
Humanitarian Measures:
Address humanitarian concerns by providing assistance to refugees and asylum seekers. Streamline asylum processes to ensure timely and fair assessments. Collaborate with international organizations to ensure a coordinated humanitarian response.
Pathways to Legalisation:
Implement pathways for undocumented immigrants to legalize their status, subject to certain criteria. Consider amnesty or regularization programs for long-term undocumented residents.
Implementing a combination of these strategies, tailored to the specific context of India, can contribute to a more comprehensive and effective approach to addressing the challenges of illegal immigration.
Addressing illegal immigration requires collaborative efforts on an international scale. Here are ways in which countries can come together to fight against illegal immigration:
Bilateral and Multilateral Agreements:
Establish bilateral and multilateral agreements between countries to cooperate on immigration issues. Define common protocols for border control, information sharing, and joint operations.
Information Sharing:
Create platforms for sharing intelligence and information related to illegal immigration. Enhance collaboration between law enforcement agencies to track and apprehend human traffickers and criminal networks.
Regional Cooperation:
Form regional alliances or organizations to address immigration challenges collectively. Share best practices and resources among neighbouring countries facing similar issues.
Joint Border Control Operations:
Conduct joint border control operations to enhance security and deter illegal crossings. Pool resources for the development of technology and infrastructure to secure shared borders.
Humanitarian Initiatives:
Develop joint humanitarian initiatives to address the root causes of migration, such as poverty, violence, and political instability. Collaborate on providing aid and support to regions.
Asylum and Refugee Policies:
Develop standardised asylum and refugee policies to ensure fair and consistent treatment. Share the responsibility of hosting and supporting refugees through international cooperation.
Diplomacy and Conflict Resolution:
Engage in diplomatic efforts to address the root causes of conflicts that contribute to migration. Promote peaceful resolutions to political and social issues that drive people to flee their home countries.
International Organisations: Collaborate with international organisations such as the United Nations and Interpol to coordinate efforts. Participate in forums and conferences focused on global migration issues to share insights and strategies.
Public Awareness Campaigns:
Conduct joint public awareness campaigns to inform potential migrants about legal avenues and the risks of illegal migration. Foster understanding among the public about the complexities of migration and the need for collective solutions. By working together on these fronts, countries can create a more coordinated and effective response to the challenges posed by illegal immigration. It requires a combination of diplomatic, legal, humanitarian, and security measures to address the complex and multifaceted nature of migration.
References
Dhankhar, L. (2022, 02 15). Donkey route flyers knew of risks, pitfalls. Retrieved from Hindustan Times: https://www.hindustantime s.com/india-news/donkey- route-flyers-knew-of-risks- pitfalls- 101704392942550.html
Dhankhar, L. (2024, 01). Forged papers, long route: Rush of FIRs reveal tip of immigration racket iceberg. Retrieved from Hindustan Times: https://www.hindustantime s.com/india-news/forged- papers-long-route-rush-of- firs-reveal-tip-of- immigration-racket- iceberg
Dhankhar, L. (2024, 01). Paid 1st tranche in2020 to embark on donkey route. Retrieved from Hindustan Times: https://www.hindustantim es.com/indianews/paid-1st- tranche-in-2020-to- embark-on-donkey-route- 101703788534236.html
Dieterich, C. (2023, 12 31). suspicion of illegal immigration. The incident highlights the spectacular increase in illegal emigration to the US. Retrieved from Le Monde: https://www.lemonde.fr/en/international/article/2023/1 2/31/the-american-dream- of-the-growing-number- of-indians-illegally- migrating-to-the- us_6390980_4.html#:~:text=The%20number%20of%2 0Indian%20migrants,wit%208%2C027%20in%20201 8%2D2019.
Economictimes. (2023, 1215). US authorities encountered with over 2 lakh illegal Indian immigrants in last 5 years: Data. Retrieved from The Economic Times: https://economictimes.indi atimes.com/nri/latest- updates/us-authorities- encountered-with-over-2- lakh-illegal-indian- immigrants-in-last-5-years- data/article show/105999743.cms Ernst, J. (2024, 01 01).
Plane detained in France sheds light on Nicaragua’s role in US migrant crisis. Retrieved from The Guardian: https://www.theguardian.co m/world/2024/jan/01/france- detained-plane-nicaragua- us-migrants- crisis#:~:text=The%20flight%2 C%20which%20left%20the,ti p%2Doff%20alleging%20hu man%20trafficking.&text=Th e%20passengers%2C%20ho wever%2C%20were%20not,b ut%20rather%20att Gupta, N. (2022, 02 11).
Shattered US dreams: How a Gujarat man died on Mexico border. Retrieved from Hindustan Times: https://www.hindustantimes. com/cities/others/shattered- us-dreams-how-a-gujarat- man-died-on-mexico- border- 101671872235479.html
Haryana youth taking donkey route to US dies in Guatemala. Retrieved from Times of India:https://timesofindia.indiati mes.com/city/jind/haryana- youth-taking-donkey-route- to-us-dies-in- guatemala/articleshow/9916 0285.cms IOM. (2023, 09 12). US-Mexico Border World’s Deadliest Migration Land Route. Retrieved from IOM UN Migration:https://www.iom.int/news/u s-mexico-border-worlds- deadliest-migration-land- route
Landa, M. (2023, 11 05). Illegal immigration thrives despite deaths and hardships. Retrieved from The Hindu: https://www.thehindu.com/ news/national/illegal- immigration-thrives- despite-deaths-and- hardships/article67498587.e ce
Lietuvnikė, M., Vasilis Vasiliauskas, A., Vasilienė- Vasiliauskienė, V., & Sabaitytė, J. (2018). Peculiarities of illegal immigrant’s intrusions into road freight transport units in the France – UK corridor. Entrepreneurship and Sus.Malkin, E. (2022).
Illegal immigration: Mexico- US border deaths. The Wall Street Journal. Patel, S. (2024, 04 05). Beyond Boundaries:
Decoding Why Gujaratis Are Obsessed With Settling Overseas. Retrieved from The Wire: https://thewire.in/labour/b eyond-boundaries- decoding-why-gujaratis- are-obsessed-with- settling-overseas/? mid_related_new Portal, M. D. (2024, 04 02). International Organization for Migration. (n.d.). Migrant deaths and disappearances. . Retrieved from Migration Data Portal: https://www.migrationdata portal.org/themes/migrant-deaths-and- disappearances



