Abstract
The use of technology within global societies has increased with the rapid rate of technological advancements in contemporary life. The Internet has successfully facilitated social connectedness and enhanced business opportunities in numerous ways. Our entire social and industrial history has been re-written and re-catalogued in over 25years. A vast number of the population has access to a smartphone, while most households have internet enabled devices. There is a growth in the digital revolution with many opportunities for economic growth, contributing to culture and wellbeing. However, with such rapid technological growth, there are digital concerns pertaining to individual and organisational risk, particularly when inputting and storing sensitive data. This study aims to understand the reasons why cyber threats are faced in contemporary life. There is an endeavour to facilitate cyber security through recommendations. A literature review is carried out within this study. Results have revealed the following reasons for cyber threats: Economy; Malware a business; Smaller organisations without cyber insurance; Human error. This study has deduced that cyber security is a vital component of contemporary life that requires global societies to educate themselves as to limit cyber- threats and attacks. Criminals wait for opportunities through online-interaction and seek to exploit societal vulnerabilities. Being vigilant while raising cyber awareness and taking responsibility is important. Therefore, it is essential for global societies to harbour a sense of cyber maturity and understand how digital technologies can cause harm. Preventative methods must be implemented to facilitate cyber security in contemporary life.
Introduction
The use of technology within global societies has increased with the rapid rate of technological advancements in contemporary life (Somani, Information Technology Challenges Faced during the Covid-19 Pandemic in Higher Education, 2021). The Internet has successfully facilitated social connectedness and enhanced business opportunities in numerous ways. Through the internet individuals have been able to engage with family, friends, businesses, employers and employees, enabling the effecting functioning of societies (Somani, Progressing Organisational Behaviour towards a New Normal, 2021). The use of social media and interactive video conferencing software has been utilised to stay connected to each other globally. A few years ago, this was unimaginable, well maybe the closest we would experience would be related through watching science fiction films. The internet has connected us all in unimaginable ways. Our entire social and industrial history has been re-written and re-catalogued in over 25years. A vast number of the population has access to a smartphone, while most households have internet enabled devices.
Individuals have worked from home during the coronavirus (covid-19) pandemic creating a working from home culture (Somani, Managing Mental Health at Work during Periods of Uncertainty, 2022). Individuals can exchange messages, pictures and reminisce on memories through virtual exchange. Many now watch television, stream music, or listen to the radio from global destinations via online resources. More than two thirds of individuals also manage finances through online mediums by downloading mobile applications. During the pandemic online shopping became widely used as retail prices grew. Even many governmental initiatives require internet connectivity. There is a growth in the digital revolution with many opportunities for economic growth, contributing to culture and wellbeing. However, with such rapid technological growth, there are digital concerns pertaining to individual and organisational risk, particularly when inputting and storing sensitive data. Over the years there has been an increase in the global annual cost of cybercrime. In 2021 approximately $1.2 billion was lost by US financial institutions as a result of ransomware attacks (Lyngaas, 2022). This was more than a 200% rise in comparison to 2020. It is predicted that the annual cost of cybercrime globally will increase to more than $8 trillion in 2023 (Esentire, 2023). “Cyber security is the application of technologies, processes, and controls to protect systems, networks, programs, devices and data from cyber attacks” and requires instant attention in contemporary life. (IT, 2023).
Objectives
This study aims to understand the reasons why cyber threats are faced in contemporary life. There is an endeavour to facilitate cyber security through recommendations. A literature review is carried out within this study.
Results and Discussion
The economy The economy is facing a global recession due to events like the covid-19 pandemic and the Russia-Ukraine war. There is an energy crisis, inflation and a disruption of supply chains affecting global economies. The inflation has an impact upon the cost of the preventative measures to reduce cybercrime and an increase in remediation costs. In addition, the identification of talented individuals to consume employment positions is a reason for concern. The decisions pertaining to company budget is related to the rate of inflation, although it is not directly linked to the number of cyber-attacks. Nevertheless, there has been a reduction in the number of talented individuals being hired as technological organisations undergo hiring freezes (Bove, 2022). With a reduction in financial availability to safeguard companies and implement sufficient security or competent teams to protect the businesses, an increase in cybercrimes is anticipated. It is likely that the number of devices connected to the Internet of All Things will reach 15.1 billion globally and approximately 36% of people will be working remotely by the year 2025 (Flynn, 2022). There were approximately 1.5 billion cyber attacks on smart devices during the first half of 2021. Attackers stole sensitive data, build botnets or cryptojack devices and continues to grow very quickly.
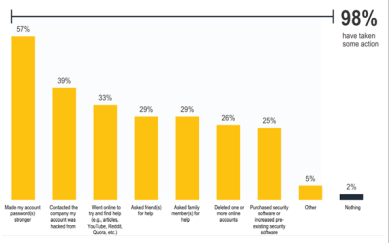
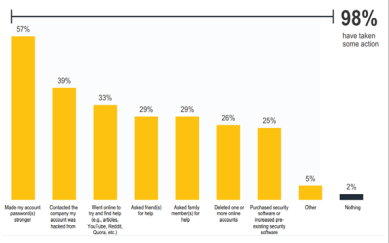
The increase in hacking is creating a trend as they take advantage of global conflicts, including the Russia- Ukraine war and ulterior motives pertaining to politics. This can be demonstrated by the increase in the number of oil and mining organisations being targeted by environmental hacktivists. This can also be referred to as hacking for a cause and considered a mainstream force. Such events have been highlighted internationally through the 2.6 TB Panama papers leak (Gross, 2016) and the Democratic National Committee email hack (Barrett, 2018). Hacktivism has been proven as a weapon or online protest and can cause chaos leading to change. Malware: a business Ransomware has become a business and a means to earn financial benefits. Within global sectors numerous businesses, governmental and non-governmental organisations, individuals have all been subjected to ransomware. Access to powerful ransomware tools have become easier to access compared to previous years. Criminals can initiate cyber-attacks with limited technical skills and attain a substantial financial gain (Reed, Ransomware-as-a-Service Transforms Gangs Into Businesses, 2022). Through an investment of approximately $66, criminals can buy malware and ransomware (Reed, It’s Not Fair, But Cyber Crime Is Cheap, 2022). In addition, currently there are underground forums that supply users with free phishing kits. Data breaching globally has reached an average cost of $4.35 million with approximately 83% of attacks experiencing more than one breach (IBM, 2022). With the ease of obtaining malware services globally, there is a risk that cyber attacks are going to increase without significant intervention for protection. The most common form of data breach is stealing or compromising credentials (IBM, 2022). 19% comprised of stolen or compromised credentials, 16% comprised of Phishing, 15% was due to cloud misconfiguration, 13% was attributed to vulnerability in third party software, 9% resulted from physical security compromise, 8% was due to a malicious insider, 7% was a system error, 6% was due to a business email compromise, 5% resulted from accidental data loss or lost device, and 3% was due to system engineering. Figure 1 illustrates that 98% of individuals have acted after detecting unauthorised access to devices or accounts and the action taken (Norton, 2021).
Smaller organisations Organisations that are smaller in size have been the target of cyber-crimes between 2020 and 2021 increasing by 150% (Jimenez, 2022). The reasons behind this are due to the fact that cyber security is weaker within smaller organisations, and stronger law enforcement responses are prevalent within larger organisations. Therefore, it is likely that organisations with less than one thousand employees will be targeted and attacked. Such organisations can include smaller businesses, governmental offices, local educational institutions, and police departments. As financial revenue is limited and budgets are tightened in contemporary life, it is likely that smaller organisations will be unable to afford cyber insurance which will leave them exposed with limited or no coverage. It is likely that new underwriting requirements will be necessary and there will be increased scrutiny of risk mitigation and security program maturity (Forrester, 2022). If cyber-attacks and breaches are successful, businesses will face immense financial pressure which may threaten future closures. It is highly likely that in 2023, there will be a rise in cyber attacks and the costs associated with it.
Human error
95% of cyber security issues have occurred due to human error. In 2023, it is predicted that the primary factor to promote cyber security threats is human error. Due to a lack of cyber security expertise and awareness, the cyber security of organisations has been compromised. . Human error contributing to cyber security threats comprises of a lack of attention or unintentional acts that result in data breaches. Such errors can include downloading infected software, creating a weak password, IP address compromises and not updating software as necessary to prevent viruses (News, 2022). When individuals learn that their devices have been accessed without authorisation, they tend to experience a variety of emotions. Figure 2 illustrates the emotions individuals felt after they found out about unauthorised access within the past year according to the World Economic Forum.
Conclusion
This study has deduced that cyber security is a vital component of contemporary life that requires global societies to educate themselves as to limit cyber- threats and attacks. Criminals wait for opportunities through online-interaction and seek to exploit societal vulnerabilities. Being vigilant while raising cyber awareness and taking responsibility is important. It is evident that cyber threats can affect organisations and individuals, they require societies to work together to be vigilant and raise awareness. It is important to take responsibility to ensure that security and success do not attract those in society that try to use this and change it to their own advantage by seeking personal profit. Cyber criminals wait for opportunities through interactions that occur online through which they seek to exploit societal vulnerabilities. Therefore, it is important for global societies in contemporary life to harbour a sense of cyber maturity to understand how digital technologies can cause harm.
Online fraud is a dominant crime being carried out within the contemporary world. Criminals have developed services using the internet for trade purposes, for example, professional technical experts can design software containing viruses that can infect internet connected devices. It is possible to receive phishing emails that appear to be from legitimate websites however they are in fact from illegitimate sources. The presence of malicious websites is also threatening, as devices are then infected with a malicious code through which cyber criminals can access data stored on devices remotely. Through this, access to sensitive bank details, the ability to steal data and commit fraud becomes prevalent. During the covid-19 pandemic global societies have seen a rise in assaults from criminals using technology to exploit the complexities and vulnerabilities of online presence. Cybercrime can also refer to cyberstalking, revenge porn, bullying, and child sexual exploitation. Risks of cyber-attacks can all be minimised by reducing vulnerabilities to protect ourselves. It is recommended to:
- Set strong passwords which will make it difficult for hackers to access personal and sensitive information. It is not recommended to repeat passwords on different sites but instead change passwords regularly. This can be compared to putting more locks on the front doors of residential premises.
- Individuals should only open trusted emails from people are known and disregard phishing emails without opening them.
- Keep anti-virus protections updated comparing it to setting our alarms at home before leaving the house.
- Use a full-service internet security suite, as individuals can be protected in real-time against emerging or existing malware. This can also include ransomware and viruses whilst protecting financial information.
- Manage social media settings as this will keep personal and private information locked. Cyber criminals can see answers to security questions through social media posts like pet names and mother’s maiden name.
- Strengthen the home network by using a strong encrypted password and a Virtual Private Network VPN. This ensures that everything leaving devices are encrypted.
- Protection against identity theft is to ensure that individuals do not give out personal information on the internet or tell anyone their password. If individuals feel that they are a victim of identity theft, then it is recommended to contact associated companies and banks where the fraud has occurred. Place fraud alerts and get credit reports and report identity theft to a governing body like the FCT.
It is the duty of individuals, businesses, and organisations to take the appropriate steps to protect themselves and create awareness on cybercrime and implement appropriate strategies to enhance cyber security in contemporary life.
DOI
https://doi.org/10.57259/GRJ5872
Research Objectives
This study aims to understand the reasons why cyber threats are faced in contemporary life. There is an endeavour to facilitate cyber security through recommendations.
Bio

Prof. Dr. Parin Somani, Director: London Organisation of Skills Development, Independent Academic Scholar, TEDx Speaker, Educator, International Motivational speaker, Author, Writer, Banker, Humanitarian, Philanthropist, Multi-International Award Winner. 8 Doctorate degrees recognised 5 times in World Book of Records, twice in India Book of Records, Asia Book of Records, Karnataka Book of Records and Golden Book of World Records. Helps global societies in Education, Women Empowerment, Youth Development. Travelled 117+ countries globally. Published 100+ educational papers, newspaper/magazine articles, 19 books, featured in 200+ videos, 300+ newspapers/ books. During COVID-19 she has educated 100,000+people globally, delivered research at Harvard University, invited by many states of Governors of India.
.
Facilitating Cyber Security in
Contemporary Life