Research Objectives:
The aim of this research is to explore the realms of organisational excellence beyond the limitations of mere skill sets. This study seeks to facilitate a deeper understanding of the untapped potentials residing within their workforce, fostering a culture centred around fulfilment and purpose-driven engagement.
Keywords:
Excellence, Potential, Fulfilment, Engagement, Leadership
Bio
Dr. Bola Benson, a seasoned consultant, coach, and speaker, is deeply committed to the transformative power of education, particularly for women.
With over 15 years of professional experience, Bola has played a pivotal role in the success of numerous brands, offering expertise in higher education, care services, and professional development training. Her unwavering passion for education and empowerment permeates her work, evident in her role as Managing Director at Global North London Business School and founder of Beyond Talent. Bola’s dedication to providing opportunities for growth and learning makes her a commendable leader in her field.
Abstract
Contemporary businesses face an evolving landscape where traditional metrics of success no longer suffice. This study delves into the paradigm shift necessitating a deeper exploration of the untapped potentials within the workforce. The research aims to transcend Dr Bola Benson Founder: Beyond Talent conventional notions of organisational success by prioritising employee fulfilment and purpose-driven engagement. Employing a comprehensive methodology, this study amalgamates insights from academic literature and industry practices to uncover talent that is present beyond conventional skill sets. Results highlight the transformative impact of recognising individual strengths, passions, and motivations on organisational dynamics.
The discussion underscores the pivotal role of leadership in fostering a culture that nurtures employee fulfilment. By aligning personal values with organisational objectives, employees transcend their roles, becoming a medium for innovation and growth. Moreover, investing in employee development not only enhances individual performance but also cultivates a vibrant organisational culture Leading companies exemplify the benefits of prioritising employee well-being and aligning organisational goals with workforce interests. By cultivating an inclusive environment and prioritising employee growth, these organisations achieve sustainable success and set new benchmarks for excellence.
In conclusion, the study advocates for a holistic approach to organisational success, one that prioritises the well-being and growth of employees. By embracing the power beyond talent, organisations can redefine success, building a brighter future for all stakeholders.
Introduction
The contemporary business world is characterised by a relentless pace of change, forcing organisations to re-evaluate traditional benchmarks of success (Owoseni, 2023). While technical skills remain a fundamental requirement, a growing body of research suggests that a sole focus on these qualifications is insufficient for achieving sustained competitive advantage (Omol, Mburu, & Abuonji, 2023). The imperative lies in acknowledging and strategically leveraging the ‘hidden potential’ residing within the workforce (Nguyen, Malik, & Budhwar, 2022). This potential extends beyond technical expertise, encompassing the unique blend of individual strengths, passions, and motivations that each employee brings to the table. Recent studies demonstrate a strong correlation between employee well-being and innovative output, highlighting the critical role of fostering an environment that unlocks this untapped potential (Wang, Chen, Wang, & Xie, 2022).
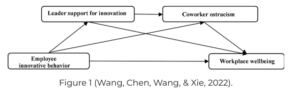
Figure 1 highlights that leader endorsement of innovation and coworker exclusion serve as mediating factors in the correlation between employee innovative behaviour and workplace well-being. Put simply, support from leaders for innovation correlates negatively with coworker exclusion, and employee innovation indirectly impacts workplace well-being through the mediating pathway of leader support for innovation–coworker exclusion. Organisations clinging to transactional employment models, focused solely on tasks and outputs, risk missing out on a wellspring of creativity and ingenuity.
Objectives
The aim of this research is to explore the realms of organisational excellence beyond the limitations of mere skill sets. This study seeks to facilitate a deeper understanding of the untapped potentials residing within their workforce, fostering a culture centred around fulfilment and purpose-driven engagement.
2.0 Methodology
This study employed a systematic literature review to delve into the concept of “power beyond talent” and its impact on organisational success. Electronic academic databases, such as Google Scholar PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science and JSTOR were utilised to conduct an extensive search.
Additionally, relevant journals and reputable sources were explored to gain a well-rounded perspective.
The keyword search strategy focused on three core themes:
Organisational Success:
“Organisational excellence,” “performance excellence,” “competitive advantage,” “high2.0 Methodology performing organisations.” Employee Fulfilment: “Employee engagement,” “employee well-being,” “workplace motivation,” “employee satisfaction.” Power Beyond Talent: “Hidden potential,” “human capital development,” “workforce potential,” “intrinsic motivation.” The search was restricted to publications within the past five years (2019- 2024) to capture the latest research in this evolving field.
A continuous review and refinement process ensured the search terms and inclusion criteria remained relevant. Articles were screened based on title, abstract, and keywords to confirm their alignment with the research objectives. Selected full texts were then evaluated for their overall relevance and methodological soundness.
This critical appraisal guaranteed the incorporation of high-quality research into the analysis.
Through this rigorous methodology, this study aims to unveil the “power beyond talent” and its potential to elevate organisational success.
By analysing existing research, the study will explore how investing in employee fulfilment and harnessing the full potential of the workforce can create a sustainable competitive advantage.
3.0 Results and Discussion
The results of this study have highlighted various aspects of the “power beyond talent” within organisations.
These insights are explored through dedicated subheadings, examining the significance of: developing talent beyond technical skills (Beyond Talent within an organisation), fostering employee fulfilment (Fulfilment in employment) and purpose-driven engagement (Purpose driven staff), and the impact of investing in staff development (Investing in staff).
3.1 Beyond Talent within an organisation
Business in contemporary life is continually evolving, and it demands a shift beyond a purely skillsbased approach to talent management. Leading organisations recognise that a vast amount of potential lies within their workforce, waiting to be discovered (Somani, 2021). This “power beyond talent” encompasses the unique blend of individual strengths, passions, and motivations that each employee brings to the table (Ntara, 2023). As leaders and decision-makers, it becomes our duty to move beyond a passive reliance on surface-level skills and qualifications. Instead, we must actively seek out and cultivate these hidden talents (Haslam, Alvesson, & Reicher, 2024).
By delving deeper into the diverse capabilities and experiences of our workforce, it is possible to promote employee’s innovation, growth, and sustained success (Sypniewska, Baran, & Kłos, 2023). Each employee possesses a unique set of skills, perspectives, and experiences that can contribute meaningfully to the collective good of the organisation (Somani, 2021). Recognising and harnessing these individual strengths lies at the heart of unleashing the full potential of teams.
Leaders as Talent Champions:
Leaders play a pivotal role in fostering an environment that unlocks the “power beyond talent.” This requires a proactive approach that involves: Regular Skill Assessments: Implementing regular assessments helps identify individual strengths and areas for development (WEF, 2024).
Investment in Skill Development: Providing opportunities for continuous learning and skill development empowers employees to enhance their capabilities (Hieu, 2020).
Platforms for Talent Showcase: Creating platforms for employees to showcase their talents and expertise fosters a culture of innovation and recognition (Zhang, Zeng, Liang, Xue, & Cao, 2023). By investing in the personal and professional development of their workforce, leaders not only enhance individual performance but also cultivate a wellspring of talent that drives collective success and contributes towards organisational excellence.
3.2 Fulfilment in employment
Fulfilment in employment is not merely a bonus; it is the foundation upon which organisational success is built (Pandya, 2024). When individuals discover true purpose and meaning in their work, they transcend the role of passive contributors, evolving into dedicated stakeholders deeply invested in the organisation’s long-term success. This profound sense of purpose fosters not only engagement and loyalty but also ignites a passion for excellence that drives high performance across all levels of the organisation (Patil, et al., 2024).
Aligning personal values with the mission and vision of the organisation creates a powerful synergy. Employees become a medium through which positive change, innovation, and growth can occur. This alignment of purpose and fulfilment forms the bases of a vibrant and thriving organisational culture, one that fosters a sense of shared responsibility and generates a way for sustained success and prosperity.
3.3 Purpose-driven staff
Purpose-driven staff are the essence, of an organisation’s success. They infuse every aspect of the workplace with a contagious energy, enthusiasm, and dedication that fuels innovation and growth (Garr & Freitag, 2020). When employees experience a sense of purpose at work, they transcend the role of mere cogs in the machine. They become passionate champions of the organisation’s mission and vision, actively contributing to achieving shared goals.
Their motivation extends far beyond the allure of financial incentives. Purpose-driven staff are driven by an intrinsic desire to make a positive impact, not just on the organisation’s bottom line, but also on the world around them (Manzoor, Wei, & Asif, 2021). This intrinsic motivation fuels a dedication to excellence and a willingness to go the extra mile, ultimately propelling the organisation towards sustainable success (Somani, UNDERSTANDING THE CONCEPT OF MOTIVATION A N D LIFE SKILLS THROUGH LITERATURE, 2021). By fostering a culture that aligns individual purpose with organisational goals, leaders can cultivate a workforce brimming with passionate change-makers who are dedicated to leaving a lasting legacy.
3.4 Investing in staff
Investing in staff is not an expense; it’s a strategic investment in the future of organisations (Li, 2022). When leaders prioritise the well-being, growth, and professional development of their employees, they unlock a wealth of potential that translates into tangible benefits.
This includes heightened productivity, a surge in innovation, and a trajectory towards sustainable growth.
By providing opportunities for continuous learning, mentorship, and career advancement, we empower our employees to reach their full potential and contribute meaningfully to the organisation’s success.
This shift in perspective is no longer theoretical. Leading companies across diverse industries have embraced this new paradigm, investing in staff and are now reaping the rewards (BRUNO, HE, HENISZ, POLLOCK, & ULRICH, 2023). By prioritising employee fulfilment and forging a strong alignment between organisational goals and the best interests of their workforce, these companies are not only achieving traditional measures of success but are also setting new standards for excellence, innovation, and social responsibility. This commitment to their human capital translates into a competitive advantage that facilitates them towards long-term prosperity.
3.5 Increasing productivity
Increasing productivity is a fundamental goal for any organisation seeking to maintain a competitive edge and drive sustainable growth. This can be achieved through a multi-pronged approach that optimises processes, streamlines workflows, and leverages technology to enhance efficiency and output across all operational levels (Rožman, Tominc, & Štrukelj, 2023). Investing in employee development plays a crucial role in this equation. By providing access to training opportunities and the latest tools and resources, organisations empower their workforce with the skills and knowledge necessary to perform at their best (Somani, Progressing Organisational Behaviour towards a New Normal, 2021). Furthermore, fostering a supportive work environment that prioritises well-being and reduces stress can significantly enhance employee engagement and motivation, leading to higher productivity.
Beyond individual capabilities, fostering a culture of accountability, clear communication, and collaboration is essential for successful teamwork.
Empowering teams to work effectively together, share knowledge, and solve problems collaboratively enables them to achieve higher levels of performance and optimise collective output. Ultimately, prioritising productivity allows organisations to maximise their resources, minimise waste, and achieve greater profitability. This not only ensures long-term success but also positions the organisation for continued growth and competitive advantage in the ever-evolving business environment.
3.6 Leading companies across industries
Leading companies across various industries have embraced a progressive approach that prioritises employee fulfilment, invests in staff development, and aligns organisational goals with employee well-being. This forward-thinking strategy reaps significant rewards. These companies consistently report increased employee engagement, a surge in innovation, and a demonstrably more positive organisational culture. According to Wellable the top ten companies setting new standards for employee engagement in 2024 include: Google, Mastercard, Cisco Systems, Rakuten, Salesforce, Apple, Kaiser Permanente, Microsoft, Society For Human Resource Management (SHRM), NVIDIA (Wellable, 2024).
By fostering a sense of purpose and fulfilment among their employees, these top performers experience tangible benefits in productivity, efficiency, and sustainable growth. They serve as shining examples of how prioritising employee well-being and investing in staff development leads not only to financial success but also to long-term viability and prosperity in today’s competitive business landscape.
A Shift in Perspective: Recognising Employees as Assets
This shift in perspective acknowledges employees not simply as workers, but as invaluable assets crucial to the company’s success (Davidescu, Apostu, Paul, & Casuneanu, 2020).
This translates into a commitment to creating a supportive and inclusive work environment that actively promotes employee well-being, professional growth, and development.
Fostering Open Communication: A Foundation for Success
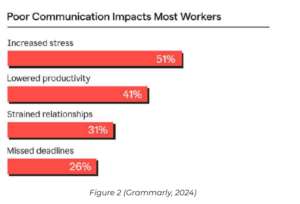
Fostering open communication channels and actively soliciting feedback from employees is essential (Kimani, 2024). This ensures their voices are heard and valued, and also helps identify areas for improvement within the organisation. By proactively looking out for the best interests of employees, organisations cultivate a sense of trust and loyalty, ultimately creating a foundation for sustained success and excellence. Figure 2 highlights the impact poor communication has on workers according to the 2024 state of business communication report.
Hence this emphasises the need for excellence communication within an organisation to thrive towards success.
Investing in People: Beyond Financial Incentives
Leading organisations strive to understand the needs and aspirations of their workforce. This goes beyond offering competitive salaries and benefits. It means providing opportunities for career advancement, skills development programmes, and promoting healthy work-life balance (Liu & Liu, 2022).
4.0 Conclusion
The relentless pursuit of financial gain, market share, and industry accolades has long been the traditional measure of organisational success. However, this study compels us to consider a more holistic perspective. True and sustainable success lies not just in financial metrics, but in the well-being and happiness of employees. As leaders, there is a fundamental responsibility to look out for the best interests of those under our care, fostering an environment where every individual feels valued, supported, and empowered to reach their full potential.
This research has shed light on the limitations of traditional, purely financial measures of organisational success. It compels us to embrace a more holistic perspective, recognising the well-being and development of our workforce as the foundation of true and sustainable success. Leaders have a critical role to play in fostering an environment that unlocks the “power beyond talent” within their employees. By nurturing a culture of purpose, fulfilment, and growth, organisations can unleash a wealth of potential for innovation, competitive advantage, and societal impact.
This shift in focus is not merely aspirational; it is a strategic imperative in today’s dynamic business world. By prioritising the human element within our organisations, we can build a future where success is not just measured by profit margins, but by the collective well-being and prosperity of our people and the communities we serve.
Based on the research findings presented in this paper, the following recommendations are offered for leaders and organisations seeking to unlock the “power beyond talent” within their workforce and redefine success through a people-centric approach:
-
Invest in Identifying and Cultivating Hidden Potential:
Implement regular skills assessments to go beyond technical expertise and uncover the unique strengths, passions, and talents that each employee possesses.
Develop and implement targeted training and development programs that cater to individual needs and aspirations, fostering continuous learning and growth.
Create platforms and opportunities for employees to showcase their talents and expertise, fostering a culture of innovation and recognition.
-
Foster a Culture of Purpose and Fulfilment:
Align organisational goals with employee values by actively soliciting employee feedback and ensuring a sense of shared purpose.
Empower employees by providing them with ownership of their work and opportunities to make meaningful contributions. Promote open communication and transparency, fostering trust and a sense of belonging within the organisation.
-
Prioritise Employee Well-being and Growth:
Implement initiatives that promote work-life balance and reduce stress, fostering a healthy and engaged workforce.
Offer opportunities for mentorship, career advancement, and professional development, empowering employees to reach their full potential. Invest in creating a supportive and inclusive work environment that celebrates diversity and fosters a sense of community.
-
Measure and Track Impact:
Develop metrics to track the impact of employee well-being initiatives on key performance indicators (KPIs) such as engagement, productivity, and innovation.
Regularly assess employee satisfaction and conduct surveys to identify areas for improvement and ensure alignment with employee needs.
Benchmark against leading companies to continuously learn and adapt best practices in fostering a thriving work environment.
By implementing these recommendations, organisations can move beyond traditional measures of success and unlock the true potential of their workforce. Investing in people is not simply an expense; it’s a strategic investment in building a sustainable future for the organisation, its employees, and the wider community.
References
BRUNO, C . , H E , A . , HENISZ, W. J., POLLOCK, J., & ULRICH, E. (2023). The People Factor HOW INVESTING IN EMPLOYEES PAYS OFF.CPP INVESTMENTS INSIGHTS INSTITUTE, FCLTGLOBAL, THE WHARTON SCHOOL.
Davidescu, A. A., Apostu, S. A., Paul, A., & Casuneanu, I. (2020). Work Flexibility, Job Satisfaction, and J o b P e r f o r m a n c e a m o n g R o m a n i a n Employees—Implications for Sustainable Human Resource Management. Sustainability.
Garr, S. S., & Freitag, K. (2020). The Purpose Driven Organization: HR’s Opportunity During Crisis & Beyond. RedThread Research.
Grammarly. (2024, 02 21). The 2024 State of Business Communication Report: What You Need To Know. Retrieved from Grammarly: https://www.grammarly. com/business/learn/introducing-2024-state-of-business-communication/
Haslam, S. A., Alvesson, M., & Reicher, S. D. (2024). Zombie leadership : Dead ideas that still walk among us. The Leadership Quarterly. Hieu, V. (2020). Employee e m p o w e r m e n t a n d empowering leader – ship: A literature review. Technium, 20-28.
Kimani, B. (2024 ). Internal Communication Strategies and Employee Engagement. Journal of Public Relations, 13-24.
Li, L. (2022). Reskilling and Upskilling the Future-ready Workforce for Industry 4.0 and Beyond. Inf Syst Front . Liu, W., & Liu, Y. (2022). The Impact of Incentives on Job Performance, Business Cycle, and Population Health in Emerging Economies. Frontiers in public health.
Manzoor, F., Wei, L., & Asif, M. (2021). Intrinsic Rewards and Employee’s Performance With the Mediating Mechanism of Employee’s Motivation. Front. Psychol.
Nguyen, T. M., Malik, A., & Budhwar, P. (2022). Knowledge hiding in organizational crisis: The moderating role of leadership. J Bus Res, 161-172.
Ntara, C. (2023). Talent management in the international business landscape. In S. Nagy, & A. M. Pelser, The improvement of Skills & Talents in the workplace. (pp. 89-113). Axiom Academic Publishers.
Omol, E., Mburu, L., & Abuonji, P. (2023). Digital maturity action fields for SMEs in developing economies. Journal of Environmental Science, Computer Science, and Engineering & Technology.
Owoseni, A. (2023). What is digital transformation? Investigating the metaphorical meaning of digital transformation and why it matters. Digital T ra n s f o r m a t i o n a n d Society, 78–96.
Pandya, J. (2024). Intrinsic & extrinsic motivation & its impact on organizational performance at Rajkot city: A review. Journal of Management Research and Analysis, 46-53.
Patil, S. S., Abraham, S., Sharma, I., Sharma, R., Prasad, J., & Gomathi, S. (2024). Exploring the Influence Mechanism of Strategic Leadership, Employee Engagement and Job Involvement; A Framework Model Approach. Journal of Informatics Education and Research, 1526-4726.
Rožman, M., Tominc, P., & Štrukelj, T. (2023). Competitiveness Through Development of Strategic Ta l e n t M a n a g e m e n t and Agile Management Ecosystems. Glob J Flex Syst Manag, 373–393.
Somani , P . ( 2 0 2 1 ) . Progressing Organisational Behaviour towards a New Normal. Journal of Economics, Finance and Management Studies, 1628-1633.
Somani , P . ( 2 0 2 1 ) . UNDERSTANDING THE CONCEPT OF MOTIVATION AND LIFE SKILLS THROUGH LITERATURE. In M. R. Rajwade, D. M. Nerkar, S. R. Kosambi, & S. S. Waghmare, The Reflections of Pandemics on Literature, Culture and Society (pp. 10-20). Mauritius: LAP.
Sypniewska, B., Baran, M., & Kłos, M. (2023). Work engagement and employee satisfaction in the practice of sustainable human resource management – based on the study of Polish employees. Int Entrep Manag J, 1069–1100. Wan g, H., Ch en, X.,
Wang, H., & Xie, M. (2022). Employee innovative behavior and workplace wellbeing: Leader support for innovation and coworker ostracism as mediators. Front. Psychol.
WEF. (2024). Putting Skills First: Opportunities for Building Efficient and Equitable Labour Markets. Geneva: World Economic Forum.
Wellable. (2024, 02 12). 15 Companies Setting New Standards For Employee Engagement In 2024. Retrieved from Wellable: https://www. wellable.co/blog/employee-engagement-companies/#h-10-nvidia
Zhang, W., Zeng, X., Liang, H., Xue, Y., & Cao, X. (2023). Understanding How Organizational Culture Affects Innovation Performance : A Management Context Perspective. Sustainability.



