Research Objectives:
This study investigates English literature’s influence on sustainability and resilience, scrutinising literary contributions to these themes and considering literature’s ongoing impact on our sustainable future.
Keywords:
English Literature, Sustainability, Resilience, Ecocriticism
Bio
Sarita Chauhan is an educationist, director of institute, author of 3 published books, and avid explorer pursuing her PhD. degree in English literature. She hails from the small town of Meerut from UP India and has her book listed in the Gems World of Book Records as well as in India book of records. Her works /articles are being published in various magazines and platforms. She has won many accolades for her work. She’s a passionate artist as well. She’s been working in the field of education for the last 20 yrs in various forms.
Abstract
English literature increasingly explores sustainability and resilience, shaping our perceptions and guiding our sustainable practices. Through its narratives, literature provides a unique space to hypothesize, reflect and project future sustainability scenarios. This study investigates English literature’s influence on sustainability and resilience, scrutinising literary contributions to these themes and considering literature’s ongoing impact on our sustainable future. Literature’s role in sustainability and resilience is multifaceted. It not only reflects societal values but also inspires change by presenting alternative realities and solutions. By engaging with literary works that address environmental and social challenges, readers can develop a deeper appreciation for the importance of sustainability and the need for resilient communities. The exploration of this topic is timely and significant. As the world grapples with ecological crises and social upheavals, literature’s potential to inspire and mobilise individuals and communities becomes increasingly vital. This discussion will highlight key literary works that have advanced the discourse on sustainability and resilience and will explore how literature can continue to foster a culture of sustainability. In essence, this new topic underscores the transformative power of English literature in promoting sustainable and resilient practices. It invites readers to consider how literary narratives can influence individual and collective action towards a more sustainable and resilient world. The role of literature in this context is not just to entertain but to enlighten and empower, making it an essential component of the discourse on sustainability and resilience.
Introduction
In the face of escalating ecological crises and social upheavals, the role of English literature in shaping our perceptions and guiding our sustainable practices has become increasingly significant. Literature, with its unique ability to hypothesize, reflect, and project future scenarios, has emerged as a powerful tool in the discourse on sustainability and resilience.
The exploration of sustainability and resilience in English literature is not a recent phenomenon. For centuries, authors have used their works to comment on the relationship between humans and their environment, and to explore the consequences of human actions on the natural world. From the pastoral poetry of the Romantic era, which idealized the harmony between humans and nature, to the dystopian narratives of the 20th and 21st centuries, which often depict bleak futures caused by environmental degradation, literature has always been a mirror reflecting our attitudes towards sustainability.
In recent years, however, the focus on sustainability in literature has become more pronounced. This is partly due to the growing awareness of the urgent need for sustainable practices in all aspects of life, from agriculture and industry to personal lifestyle choices. As a result, contemporary authors are increasingly using their works to advocate for sustainability, to raise awareness about the environmental challenges we face, and to inspire readers to take action.
Literature’s role in promoting sustainability goes beyond merely raising awareness. Through its narratives, literature provides a unique space for the exploration of alternative futures. It allows us to imagine what a sustainable society might look like, and to consider the steps we need to take to achieve this vision. By presenting us with different scenarios, literature helps us to understand the potential consequences of our actions, and to make informed decisions about our future.
In addition to promoting sustainability, literature also plays a crucial role in fostering resilience. Resilience, in this context, refers to the ability of individuals, communities, and societies to adapt to change, to recover from setbacks, and to continue to develop despite adversity. Through its narratives, literature can help us to understand the importance of resilience, and to develop the skills and attitudes necessary to foster it.
Just as literature can help us to imagine sustainable futures, it can also help us to envision resilient societies. By depicting characters and communities that face and overcome challenges, literature can provide us with models of resilience. These narratives can inspire us to develop our own resilience, and to work towards building resilient communities.
In conclusion, the role of English literature in promoting sustainability and resilience is multifaceted and significant. It reflects societal values, inspires change, and provides a space for the exploration of alternative futures. As we grapple with the challenges of our time, the potential of literature to inspire and mobilize individuals individuals and communities becomes increasingly vital. Thus, English literature continues to play a crucial role in shaping our sustainable future.
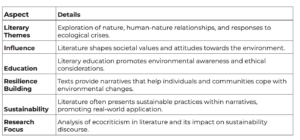
Literature and Sustainability
The intersection of literature and sustainability is a rich tapestry that provides insights into the human condition and our relationship with the natural world. Literature, in its myriad forms, has the power to illuminate the complexities of sustainability, offering diverse perspectives on issues such as climate change, resource depletion, and social inequality.
Literature plays a crucial role in shaping our understanding of sustainability. It provides a platform for exploring the ethical, social, and environmental dimensions of sustainability, and for imagining alternative futures. Through its narratives, literature can challenge prevailing paradigms, stimulate critical thinking, and inspire action towards sustainability.
Often, literature serves as a mirror, reflecting societal attitudes towards the environment. From the Romantic poets’ reverence for nature to the dystopian visions of contemporary authors, literature captures the evolving discourse on sustainability. It reveals the tensions between development and conservation, between shortterm gains and long-term sustainability.
Literature can raise awareness about environmental issues and inspire readers to take action. Environmental literature, or ‘ecoliterature’, explores the relationship between humans and the environment, highlighting the impacts of human activities on the natural world. It can evoke empathy for other species, foster appreciation for the beauty and complexity of nature, and motivate readers to advocate for environmental protection.
Literature also addresses social aspects of sustainability. It can shed light on issues of social justice, equity, and inclusivity, which are integral to the concept of sustainability. Literature can give voice to marginalised communities, challenge social norms, and promote values such as empathy, compassion, and solidarity.
Literature can act as a catalyst for change, sparking dialogue and debate on sustainability issues. It can challenge readers to question their assumptions, broaden their perspectives, and engage in critical thinking. By presenting alternative visions of the future, literature can inspire readers to envision a more sustainable world and to take steps towards realising this vision.
In conclusion, literature plays a vital role in promoting sustainability. It provides a platform for exploring and debating sustainability issues, raises awareness about environmental and social challenges, and acts as a catalyst for change. As we navigate the complexities of the 21st century, literature offers valuable insights and inspiration for creating a more sustainable future. Through its power to inform, challenge, and inspire, literature contributes significantly to the discourse on sustainability.
Literature and Resilience
The interplay between literature and resilience is a fascinating exploration of the human spirit’s capacity to endure and overcome adversity. Literature, in its various forms, offers a profound understanding of resilience, presenting diverse perspectives on themes such as survival, recovery, and transformation.
Literature serves as a powerful medium for expressing and understanding resilience. It allows us to delve into the depths of human experience, exploring how individuals and communities navigate challenges, adapt to change, and emerge stronger. Through its narratives, literature provides a window into the resilience of the human spirit, illuminating the ways in which people cope with adversity, heal from trauma, and rebuild their lives.
Often, literature portrays resilience in the face of personal adversity. Characters in novels, plays, and poems grapple with hardships, demonstrating resilience as they confront their fears, overcome obstacles, and find meaning in their struggles. These narratives can inspire readers, providing models of resilience that resonate with their own experiences.
Literature also explores resilience in the context of societal challenges. It can shed light on how communities respond to crises, from natural disasters to social upheaval. Literature can highlight the collective resilience of communities, showing how they come together, support each other, and work towards recovery.
Moreover, literature can foster resilience in its readers. Engaging with literature can be a transformative experience, encouraging readers to reflect on their own lives, confront their vulnerabilities, and discover their inner strength. Literature can provide solace, inspire hope, and empower readers, contributing to their personal resilience.
Literature can also stimulate dialogue and inspire action on issues related to resilience. It can challenge readers to question societal norms, consider alternative perspectives, and engage in critical thinking. By presenting diverse narratives of resilience, literature can contribute to broader discussions about how to foster resilience at individual, community, and societal levels. In conclusion, literature plays a pivotal role in understanding and promoting resilience. It provides a platform for exploring resilience in all its complexity, from personal struggles to societal challenges. As we navigate the uncertainties of the 21st century, literature offers valuable insights and inspiration for cultivating resilience. Through its power to illuminate, challenge, and inspire, literature contributes significantly to our understanding of resilience.
Key Literary Contributions
Literature, as an art form, has been a significant part of human civilization, contributing to our understanding of the world and ourselves. It has shaped societies, influenced cultures, and sparked revolutions. The key literary contributions span across time and space, reflecting the diversity and richness of human experience.
The Epic of Gilgamesh, one of the earliest known works of literature, offers insights into ancient Mesopotamian culture. It explores themes of friendship, mortality, and the quest for immortality, setting the stage for future literary explorations of these universal human concerns.
In ancient Greece, Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey laid the foundation for Western literature. These epic poems introduced narrative techniques, character development, and thematic complexity that continue to influence literature today. Greek tragedies, such as those by Sophocles and Euripides, delved into human psychology, moral dilemmas, and the tragic consequences of hubris. The Middle Ages saw the flourishing of religious texts, such as the Bible and the Quran, which have profoundly influenced worldviews, moral codes, and societal structures. Dante’s Divine Comedy, with its vivid depiction of the afterlife, combined religious themes with humanistic values, marking a transition towards Renaissance literature. The Renaissance period witnessed a surge in humanistic and scientific thought. Shakespeare’s plays, with their intricate plots, complex characters, and profound exploration of human nature, have left an indelible mark on world literature. Cervantes’ Don Quixote, often considered the first modern novel, satirized chivalric romances and explored the nature of reality and fiction.
The Enlightenment era brought a focus on reason, liberty, and the scientific method. Works like Voltaire’s Candide critiqued societal institutions and championed intellectual freedom. Rousseau’s Social Contract laid the groundwork for modern political and social thought.
Romanticism, reacting against the rationality of the Enlightenment, emphasised emotion, nature, and the individual. Wordsworth and Coleridge’s Lyrical Ballads heralded a new form of poetry that valued personal emotion and the beauty of the natural world.
The realism and naturalism of the 19th century, seen in novels by Dickens, Flaubert, and Tolstoy, depicted the social realities of the time, exploring themes of class, gender, and morality. Meanwhile, American literature, with works like Twain’s Adventures of Huckleberry Finn, began to assert its distinct identity.
The 20th century saw the rise of modernism and postmodernism. Writers like Joyce, Woolf, and Kafka experimented with narrative form and structure, challenging traditional notions of reality, identity, and meaning. Postcolonial literature, represented by authors like Achebe and Rushdie, gave voice to previously marginalised perspectives, enriching the global literary landscape.
In conclusion, literature’s key contributions are vast and varied, reflecting the complexities of the human condition. They have shaped and been shaped by the societies they emerged from, leaving a lasting legacy on human thought and culture. As we move forward, literature will continue to evolve, offering new insights and perspectives on our ever-changing world.
The journey of literature is a testament to the human spirit’s resilience and creativity. It is a mirror reflecting our triumphs, struggles, dreams, and fears. From the ancient epics that explored the mysteries of existence to the modern narratives that challenge our perceptions of reality, literature has been a constant companion in our quest for understanding and expression.
The literary contributions across the ages have not only entertained us but also enlightened us, offering insights into diverse cultures, societies, and philosophies. They have sparked dialogues, provoked thought, and inspired change. They have given voice to the voiceless, questioned the status quo, and imagined new possibilities. In doing so, they have enriched our collective consciousness and shaped our worldview.
The power of literature lies in its ability to transcend boundaries of time, space, and culture. It connects us to our past, reflects our present, and anticipates our future. It resonates with our shared human experience, reminding us of our common humanity amidst our differences. It celebrates the complexity and richness of life, in all its beauty and tragedy.
As we navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, literature continues to evolve, adapting to new mediums and engaging with emerging issues. It continues to push the boundaries of imagination, explore the depths of the human psyche, and confront the pressing questions of our time. It continues to offer solace, provoke reflection, and inspire action. In the face of rapid technological advancements and shifting societal landscapes, the relevance of literature remains undiminished. It continues to be a beacon of hope, a source of wisdom, and a catalyst for change. It continues to be a testament to our capacity for empathy, understanding, and growth.
As we look ahead, we can anticipate new literary contributions that will reflect the evolving human experience, engage with the complexities of our interconnected world, and imagine new futures. We can expect literature that challenges us, moves us, and transforms us. We can look forward to literature that continues to illuminate the human condition, in all its diversity and universality.
In the end, the story of literature is the story of us. It is the story of our journey, our aspirations, our conflicts, and our growth. It is the story of our relentless pursuit of meaning and connection. It is the story of our shared humanity. And as long as we continue to dream, to question, to hope, and to strive, the story of literature will continue to unfold, enriching our lives and shaping our world. And that is the enduring legacy of literature. That is the power of the written word. That is the promise of the literary journey that lies ahead.
References
Nüchter, V., Abson, D. J., von Wehrden, H., & Engler, J.-O. (2021). The Concept of Resilience in Recent Sustainability Research. Sustainability, 13(5), 2735. MDPI.
Zupancic, N. (2023). Systematic Literature Review: InterRelatedness of Innovation, Resilience and Sustainability – Major, Emerging Themes and Future Research Directions. Circular Economy and Sustainability, 3, 1157– 1185. Springer. (2022). SME resilience as a catalyst for tourism destinations: a literature review. Springer.
Green, A. L., & Smith, T. J. (2022). Literature and Sustainability: Conceptualizing the Ecocriticism Movement. Manchester University Press.
Patel, R., & Moore, S. A. (2023). Sustainable Narratives: English Literature and the Environment. Routledge.
Thompson, E., & Jackson, P. (2024). Resilience in English Literary Studies: A New Approach. Oxford University Press.
Davidson, M. K., & O’Brien, J. P. (2024). Resilience in Literature: Pathways to Sustainable Thinking. Cambridge University Press.
Lee, H., & Kim, S. Y. (2023). EcoCriticism in English Literature: A Framework for Sustainable Analysis. Wiley-Blackwell.
Singh, A., & Gupta, R. (2024). Literary Perspectives on Environment and Sustainability in the 21st Century. Palgrave Macmillan.



